In 2023, the equities and bond markets experienced a positive shift, while commodities faced challenges, emerging as one of the major underperformers.
The SP500 showed remarkable resilience, recording a gain of 24.7% for the year. Simultaneously, Dow Jones exhibited a solid performance, rising by 13.7%, while the NASDAQ Composite emerged as the standout performer, boasting gains of 44.5% in 2023.
The U.S. Aggregate Bond Index returned 4.7%. Commodities (S&P GSCI), faced a tough time, experiencing a downturn of 9.4%. This decline was primarily led by drops in Nickel and Zinc prices.
At the onset of 2023, markets were shrouded in pessimism due to concerns over high inflation and the Federal Reserve aggressively raising interest rates, setting the stage for a challenging year. However, the unforeseen unfolded—2023 defied expectations as it evolved into a year marked by robust market performance and an unexpected reduction in inflation. Contrary to fears, a recession failed to materialize, with markets generating strong returns against a backdrop of declining inflation rates.
Major Themes
The pivotal drivers shaping the market landscape in 2023 revolved around inflation and interest rates. The prior year, 2022, witnessed a staggering inflation surge in the United States, hitting levels unseen in four decades. Consequently, the Federal Reserve embarked on an unprecedented campaign of raising interest rates to counter this surge.
At the onset of 2023, inflation exhibited a notable decline, subsiding to 6.5% in January from its peak of 9.1% in June 2022. By year-end, inflation further moderated to 3.2%, aligning more closely with the Fed’s target of 2%. Simultaneously, the Federal Reserve altered its strategy, slowing the pace of interest rate hikes. After the historical surge that brought rates to 4.3% in 2022, the Fed increased the fed funds rate by an additional 100 basis points in 2023, bringing it to 5.3%.
Projections now indicate an anticipated shift in the Fed’s policy, with expectations of a cumulative 75-basis-point cut in interest rates slated for the following year.
Top Performers
In 2023, technology stocks made a resounding comeback, notably led by the renowned “Magnificent 7” comprising Apple, Amazon, Alphabet, NVIDIA, Meta, Microsoft, and Tesla. Among these powerhouses, NVIDIA surged by 230%, while Meta boasted a 200% increase in its stock values over the year.
These tech giants, having experienced a 39% decline collectively in 2022, staged a remarkable recovery, collectively rising by approximately 70% year-to-date in 2023. Their influence was so substantial that if their performance were excluded from the S&P 500 index, the index itself would show a more modest gain of around 6%.
Major Events
2023 was hardly bereft of events that affected the markets significantly. Despite apprehensions regarding inflation, escalating interest rates, an unforeseen regional banking crisis, and heightened global geopolitical tensions, the U.S. economy displayed resilience, witnessing an upturn in corporate profits. Here is a recap of the major events during the year.
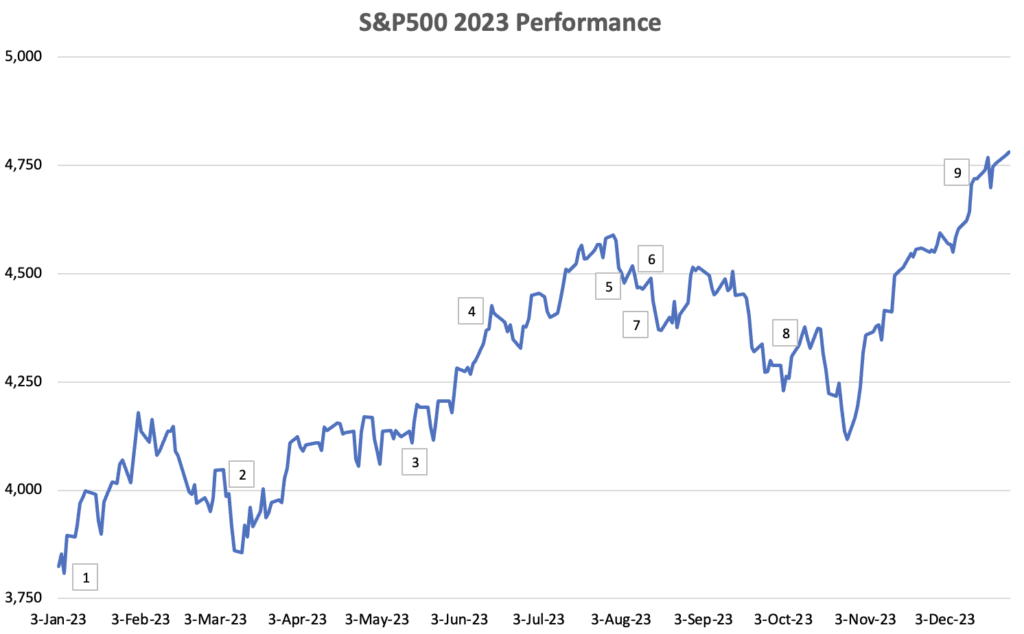
1. China ends zero COVID policy
On January 8th, China made a significant announcement signaling the end of its zero-COVID policy. This decision brought immense relief to strained supply chains and acted as a catalyst in bolstering the global economy.
2. Regional Bank crises
Mounting losses from cryptocurrency, bond, and real estate investments, along with aggressive bank deposit withdrawals, led to the collapse of Silvergate Bank, Silicon Valley Bank, Signature Bank, and First Republic Bank in a matter of weeks. This triggered a sharp decline in U.S. regional bank stock prices as investor confidence waned amid fears of potential contagion across other banks.
The Federal Reserve’s intervention averted a more severe banking crisis. By providing emergency loans to distressed banks and assuring customers of full deposit recovery—even beyond the $250,000 insured by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation—the Fed mitigated broader financial turmoil. Additionally, JP Morgan’s acquisition of First Republic Bank offered further support to the U.S. financial system.
3. NVDA’s earnings spark surge in AI investments
On May 25, 2023, Nvidia surged by 24% following an exceptional earnings report that surpassed consensus estimates. This substantial increase edged Nvidia closer to achieving a trillion-dollar valuation. Central to its remarkable growth was the widespread adoption of AI by corporations, with Nvidia’s chips leading the forefront of AI implementation across various sectors.
Investors were drawn to AI-related stocks due to the optimistic outlook that AI could significantly enhance revenue and streamline costs for a multitude of companies, further fueling enthusiasm for Nvidia and similar investments.
4. FED pauses Hikes
At its June meeting, the Federal Reserve maintained unchanged interest rates for the first time since March 2022, signaling a potential conclusion to the Fed’s tightening measures. The decision aimed to alleviate pressure on regional banks grappling with longer-term assets. This move was well received by the markets, prompting a robust rally in response.
5. Final FED hike
On July 26, the Federal Reserve increased its benchmark lending rate by a quarter point, marking the highest level reached in 22 years. Despite this hike, the Fed maintained the target range of the federal funds rate at a steady 5 percent to 5.25%.
6. Fitch downgrade US credit rating from AAA to AA+
On August 1, 2023, Fitch downgraded the United States of America’s Debt Rating from ‘AAA’ to ‘AA+’. This decision was based on the anticipated fiscal deterioration over the next three years, a substantial and escalating general government debt burden, and concerns regarding governance erosion. The market reacted with soured sentiments as the unfolding fiscal drama in the US Debt standoff continued to impact investor confidence.
7. CPI accelerates
In August, inflation surged for the second consecutive month, rebounding from earlier declines as consumers faced persistent increases in everyday expenses. Prices surged by 3.7% compared to the same period last year, outpacing both July’s 3.2% and the 3.6% estimate predicted by Refinitiv economists. Market turbulence ensued as concerns heightened over the Federal Reserve’s potential continuous tightening, leading to a decline in market confidence.
8. Israel-Hamas war
Amidst signs of market recovery, a fresh geopolitical crisis emerged as militant groups launched a surprise attack on southern Israel from the Gaza Strip on October 7. This event marked the onset of the most substantial military escalation in the region since the Yom Kippur War in 1973. As a result, oil prices surged, US treasuries reached a record high of 5%, and market sentiments continued to plummet sharply.
9. Fed said rate cuts over
On December 13, the Federal Reserve opted to keep interest rates unchanged. Jerome Powell indicated that the historic tightening of monetary policy might be concluding, citing a quicker-than-anticipated decline in inflation and the possibility of discussions regarding reductions in borrowing costs. This decision was warmly embraced by the markets, leading to record highs for all the major indexes, including the US 10-year yield dropping to as low as 3.8%.
2024 Outlook
1. Stocks will likely march to new highs: A soft landing, with moderate inflation, strong growth, and supportive policies, offers an ideal setting for stocks. If data continues to surpass expectations, valuations may rise, allowing for expansion, and potentially leading to earnings exceeding the usual growth rate. This sets a positive outlook for the stock market.
2. Bonds are Attractive Again: Bonds are currently as competitive with stocks as they were before the 2008 crisis. Given the promising returns from bonds, allocating a larger portion of an investment portfolio to fixed-income investments makes sense. Prioritizing downside risk mitigation and narrowing potential outcomes could suggest a shift towards increased bond exposure. However, for those seeking to maximize upside potential, maintaining a portfolio tilted towards stocks might be preferable.
3. Some Commodities are Attractive: Policies focusing on industrial development and the shift toward clean energy might drive up commodity prices. Historically, gold tends to perform favorably in a declining interest rate climate.
4. Economic Outlook: While a growth slowdown might be anticipated in the first half of 2024, indications suggest a resumption of growth in the latter half of the year.
5. Interest Rates: The Fed is likely to initiate interest rate cuts in the latter part of 2024. If these cuts are prompted by stabilized inflation rather than a recession, the rate reduction cycle is expected to proceed at a more gradual pace compared to previous cycles.





